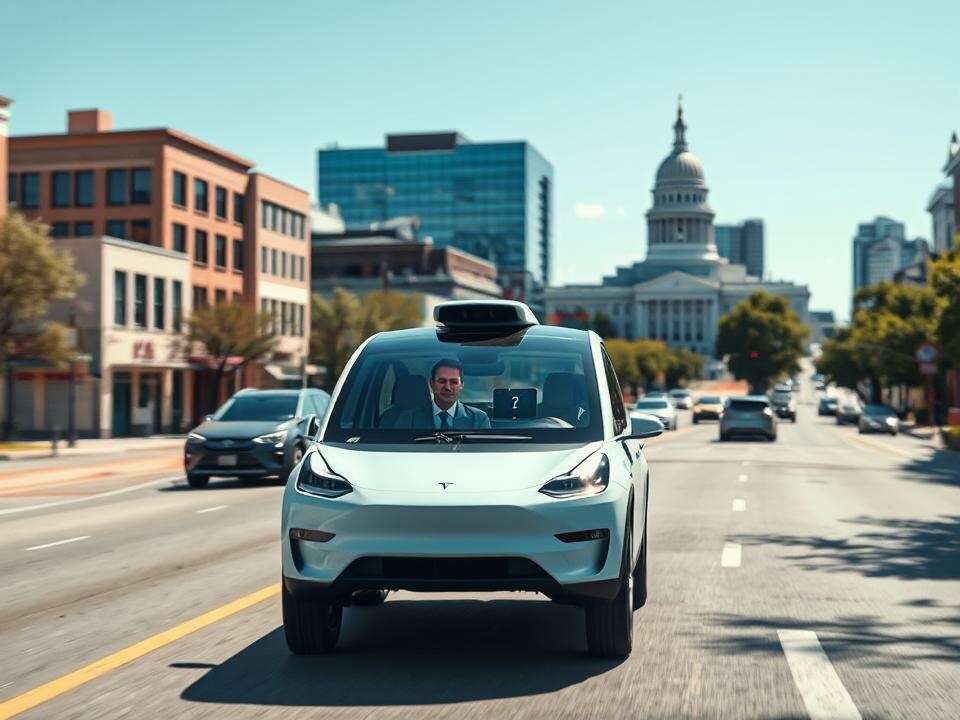
Tesla is predicted to tiptoe into its long-awaited robotaxi service in Austin, Texas, as quickly as Sunday with about 10 of its Mannequin Y SUVs that can function inside strict limits. CEO Elon Musk has mentioned the corporate is being “tremendous paranoid” about security and that people will remotely monitor the fleet.
Distant entry and management – identified within the business as “teleoperation” – is utilized in various levels by the handful of robotaxi startups working across the globe. The know-how has clear benefits and vital limitations.
Listed here are some particulars of the way it works:
WHAT IS TELEOPERATION?
Teleoperation is the management of machines by people in a unique location, often over a wi-fi community.
It’s used to coach robots to function autonomously, monitor their autonomous exercise, and take over when required.
HOW DO ROBOTAXI OPERATORS USE TELEOPERATION?
The worldwide robotaxi business remains to be in take a look at mode, as firms deploy the automobiles in restricted geographic areas and frequently regulate the synthetic intelligence software program that controls them. Teleoperation is usually used to intervene when a automobile is not sure of what to do.
Alphabet’s Waymo, for instance, has a staff of human “fleet response” brokers who reply to questions from the Waymo Driver – its bot.
“Very like phone-a-friend, when the Waymo automobile encounters a selected scenario on the highway, the autonomous driver can attain out to a human fleet response agent for added data,” Waymo mentioned in a weblog publish final 12 months.
Former Waymo CEO John Krafcik instructed Reuters, “the vehicles aren’t being actively monitored,” including that the software program is “the final word decision-maker.”
A Waymo video reveals a automobile asking a distant operator whether or not a road with emergency response automobiles is open to visitors. When the human says sure, the automobile proceeds.
In distinction, different firms, comparable to Baidu’s Apollo Go in China, have used absolutely distant backup drivers who can step in to nearly drive the automobiles. Baidu declined to remark.
WHAT ARE THE LIMITATIONS?
Driving automobiles remotely on public roads has a serious potential drawback: it depends on mobile information connections that may drop or function with a lag, disconnecting the automobile from the distant driver in harmful conditions.
Philip Koopman, a Carnegie Mellon College engineering professor and autonomous-vehicle security professional, mentioned that method might work for a small take a look at deployment of 10 automobiles, comparable to Tesla’s preliminary effort in Austin, however he referred to as teleoperation “inherently unreliable know-how.”
“Ultimately you’ll lose connection at precisely the worst time,” he mentioned. “In the event that they’ve carried out their homework, this may not ever occur for 10 vehicles. With 1,000,000 vehicles, it may occur day-after-day.”
Former Waymo CEO Krafcik agreed, including that the time delay in cell sign makes distant driving “very dangerous.”
However, counting on the automobile to succeed in out for assist and permitting the automobile to be the decision-maker are dangerous as properly, Koopman mentioned, because it doesn’t assure the automobile will make the fitting resolution.
Waymo declined to touch upon the restrictions of its method.
Koopman additionally famous there are limits to what number of automobiles one individual can safely monitor.
A bunch of Democratic Texas lawmakers requested Tesla on Wednesday to delay its robotaxi launch till September, when a brand new autonomous-driving regulation is scheduled to take impact. The Austin-area lawmakers mentioned in a letter that delaying the launch “is in one of the best curiosity of each public security and constructing public belief in Tesla’s operations.”
WHAT IS TESLA’S APPROACH?
Musk for years has promised, with out delivering, that its Full Self-Driving (Supervised) superior driver help software program would graduate to utterly self-driving and management robotaxis. This 12 months, he mentioned Tesla would roll out a paid service in Austin underpinned by an “unsupervised” model of the software program.
“Teslas might be within the wild, with nobody in them, in June, in Austin,” Musk instructed analysts and traders in January. In Might, he instructed CNBC that the robotaxi would solely function in components of Austin which can be secure for it, would keep away from tough intersections, and would use people to watch the automobiles.
What these teleoperators will do isn’t clear.
For years inside Tesla, firm executives have anticipated to make use of teleoperators who might take over in case of bother, mentioned one individual conversant in the matter. As an illustration, if a robotaxi had been caught in a crowded pedestrian space and confused about what to do subsequent, a human teleoperator might take over and information it, the supply mentioned.
Tesla marketed for teleoperation positions, saying the corporate wants the power to “entry and management” autonomous automobiles and humanoid robots remotely. Such staff can “remotely carry out advanced and complex duties,” it mentioned within the ads.
Tesla didn’t reply to a request for remark.
“We’re being tremendous paranoid about security, so the date might shift,” Musk mentioned in a publish on X final week whereas offering a tentative launch date of June 22.