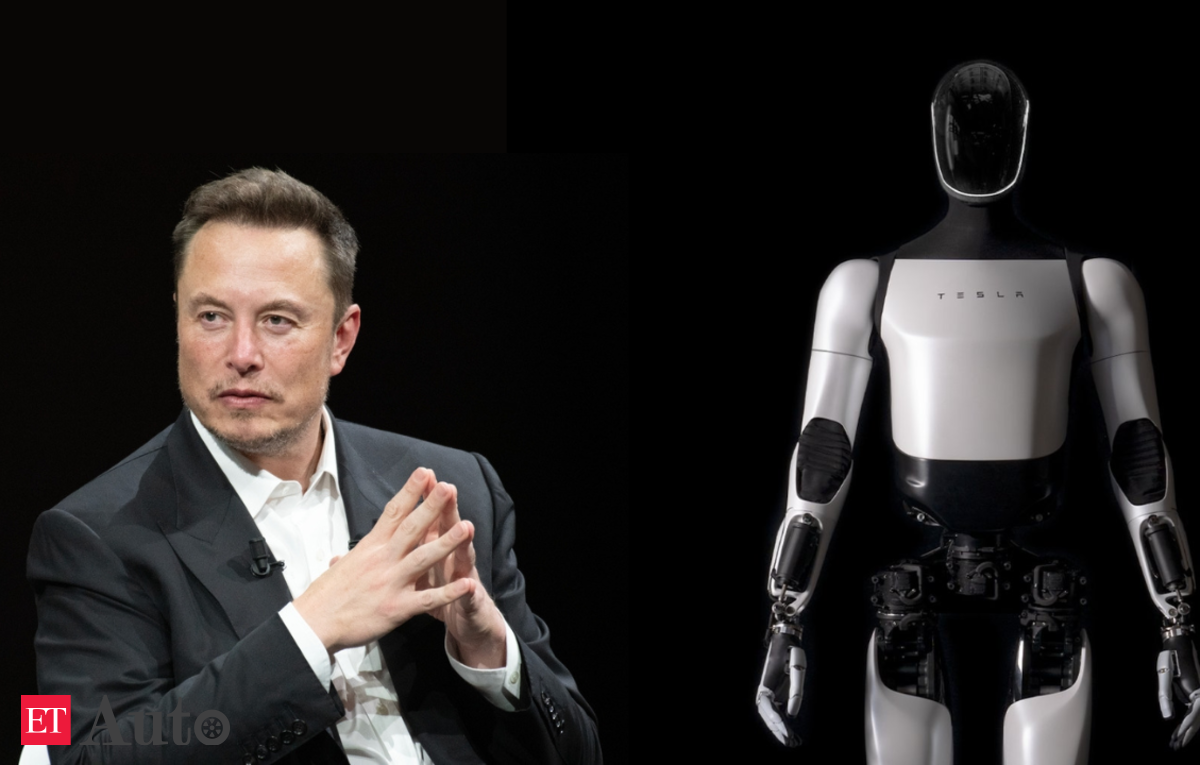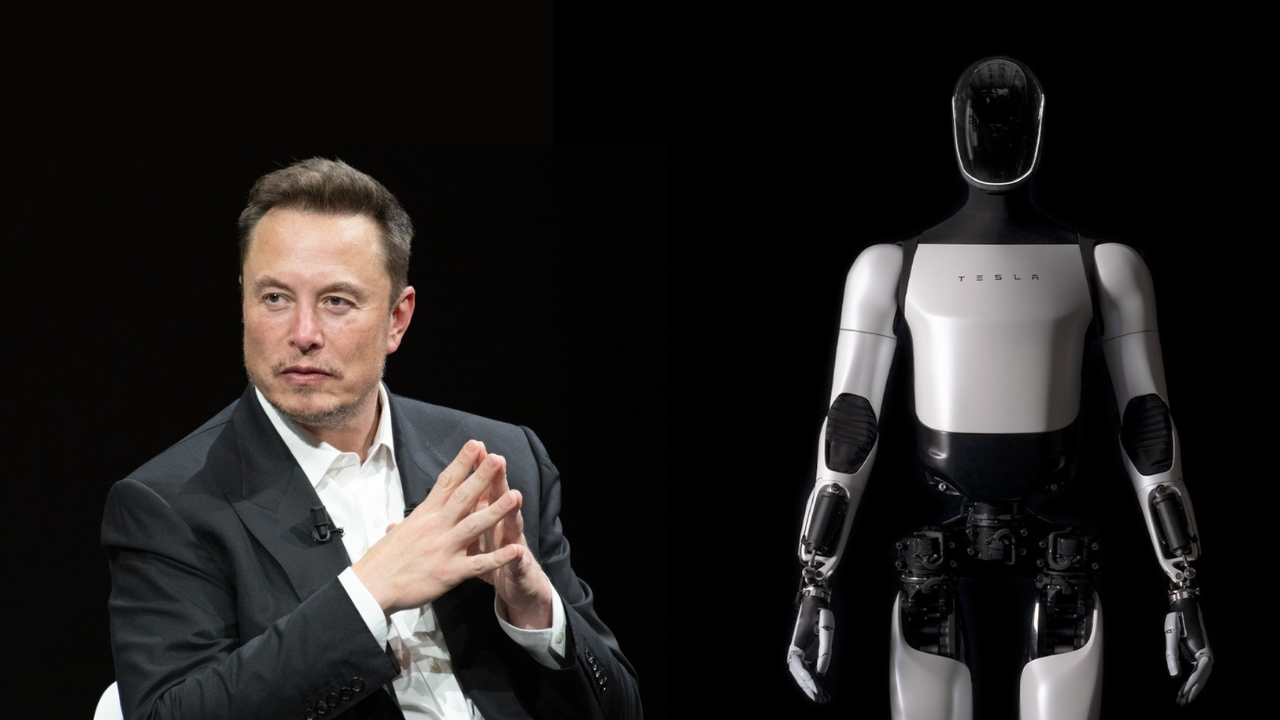
China dominates the marketplace for electrical automobiles. Now it is chasing Tesla within the race to construct battery-powered humanoids anticipated to exchange human employees constructing EVs on meeting traces.
On the World Robotic Convention this week in Beijing, over two dozen Chinese language firms confirmed off humanoid robots designed to work in factories and warehouses, with much more displaying the made-in-China precision elements wanted to construct them.
China’s push into the rising business attracts from the formulation behind its preliminary EV drive greater than a decade in the past: authorities help, ruthless worth competitors from a large discipline of recent entrants and a deep provide chain.
“China’s humanoid robotic business demonstrates clear benefits in supply-chain integration (and) mass manufacturing capabilities,” mentioned Arjen Rao, analyst at China-based LeadLeo Analysis Institute.
The robotics effort is backed by President Xi Jinping’s coverage of growing “new productive forces” in expertise – some extent made in brochures for this week’s occasion.
The town of Beijing launched a $1.4 billion state-backed fund for robotics in January, whereas Shanghai introduced in July plans to arrange a $1.4 billion humanoid business fund.
The robots on show this week draw from a few of the similar home suppliers that rode the EV wave, together with battery and sensor producers.
Goldman Sachs forecast in January the annual international marketplace for humanoid robots would attain $38 billion by 2035, with practically 1.4 million shipments for shopper and industrial functions. It estimated the price of supplies to construct them had fallen to about $150,000 every in 2023, excluding analysis and improvement prices.
“There’s huge room to squeeze the fee down,” mentioned Hu Debo, CEO of Shanghai Kepler Exploration Robotics, an organization he co-founded final yr impressed by Tesla’s humanoid robotic Optimus.
“China specialises in quick iteration and manufacturing.”
Hu’s firm is engaged on its fifth model of a employee robotic to trial in factories. He expects the gross sales worth to be lower than $30,000.
‘Catfish impact’ involves robots
When Tesla opened its Shanghai manufacturing facility in 2019, Chinese language officers mentioned they anticipated the EV pioneer would have a “catfish impact” on China’s business: introducing a big competitor that will make Chinese language rivals swim quicker.
Tesla’s Optimus robotic has had the same impact, Hu mentioned.
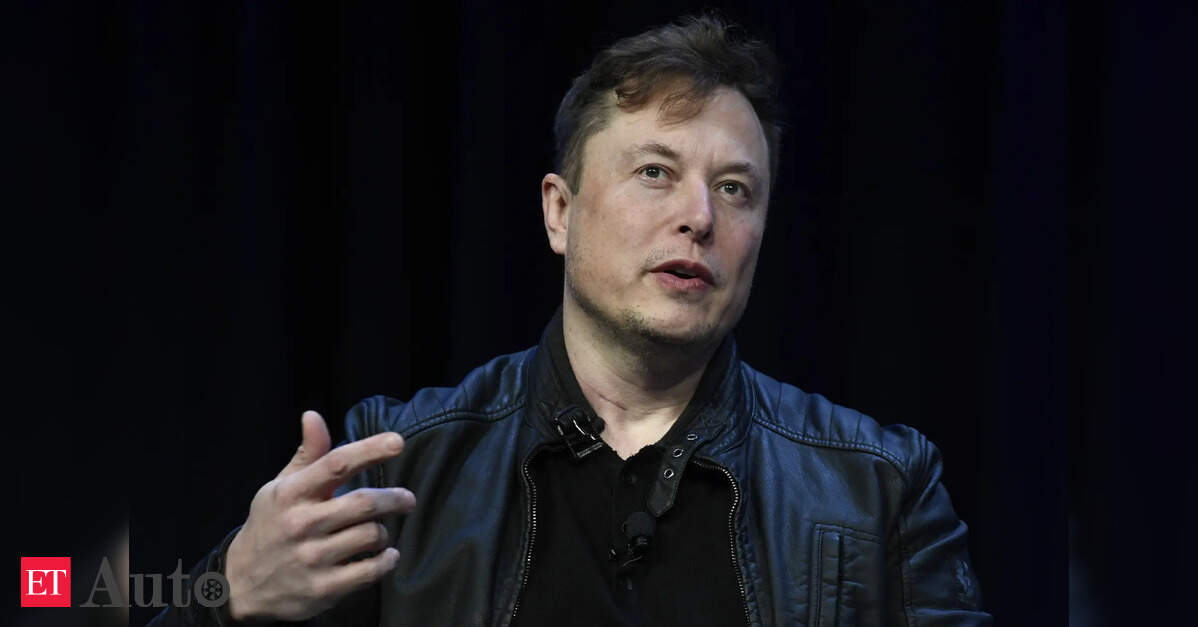
The US automaker first launched Optimus in 2021, which CEO Elon Musk then touted as doubtlessly “extra vital than the car enterprise over time”.
Musk’s firm is utilizing a synthetic intelligence strategy for Optimus modelled on its “Full Self-Driving” software program for EVs. Chinese language rivals and analysts say Tesla has an early lead in AI, however China has the flexibility to drive down the value of manufacturing.
Tesla confirmed off Optimus, mannequin-like, standing in a plexiglass field subsequent to a Cybertruck at an exhibition alongside the convention in Beijing this week.
Optimus was outdone by many Chinese language humanoids that have been waving, strolling and even shrugging, nevertheless it was nonetheless some of the well-liked reveals and thronged with individuals taking images.
“Subsequent yr there can be greater than 1,000 of my compatriots within the manufacturing facility,” an indication subsequent to Optimus mentioned.
Tesla, in an announcement, reiterated it anticipated to maneuver past prototypes to start out producing Optimus in small volumes subsequent yr.
Robots on the meeting line
Hong Kong-listed UBTECH Robotics has additionally been testing its robots in automobile factories. It began with Geely and introduced a deal on Thursday to check them at an Audi plant in China.
“By subsequent yr our objective goes to mass manufacturing,” mentioned Sotirios Stasinopoulos, UBTECH’s mission supervisor.
That will imply as much as 1,000 robots working in factories, he mentioned. “It’s the first milestone in direction of a large-scale deployment.”
UBTECH makes use of Nvidia chips in its robots however greater than 90% of elements are from China.
The present technology of manufacturing robots – huge arms able to welding and different duties – has been led largely by firms exterior China, together with Japan’s Fanuc, Swiss engineering group ABB and Germany’s Kuka, owned by Chinese language dwelling equipment producer Midea.
China leads the world with factory-installed manufacturing robots, greater than triple the quantity in North America, in response to the Worldwide Federation of Robotics.
Xin Guobin, China’s vice-minister for business and data expertise, mentioned on the opening of the Beijing occasion that his ministry had been implementing Xi’s steerage and had made China “an essential pressure within the international robotic business.”
The nation final November referred to as for mass manufacturing of humanoid robots by 2025, however that can begin on a a lot smaller scale than is required to rework EV manufacturing.
“I imagine that it’s prone to be no less than 20 to 30 years earlier than humanoid robots can obtain large-scale business utility,” mentioned LeadLeo Analysis Institute’s Rao.