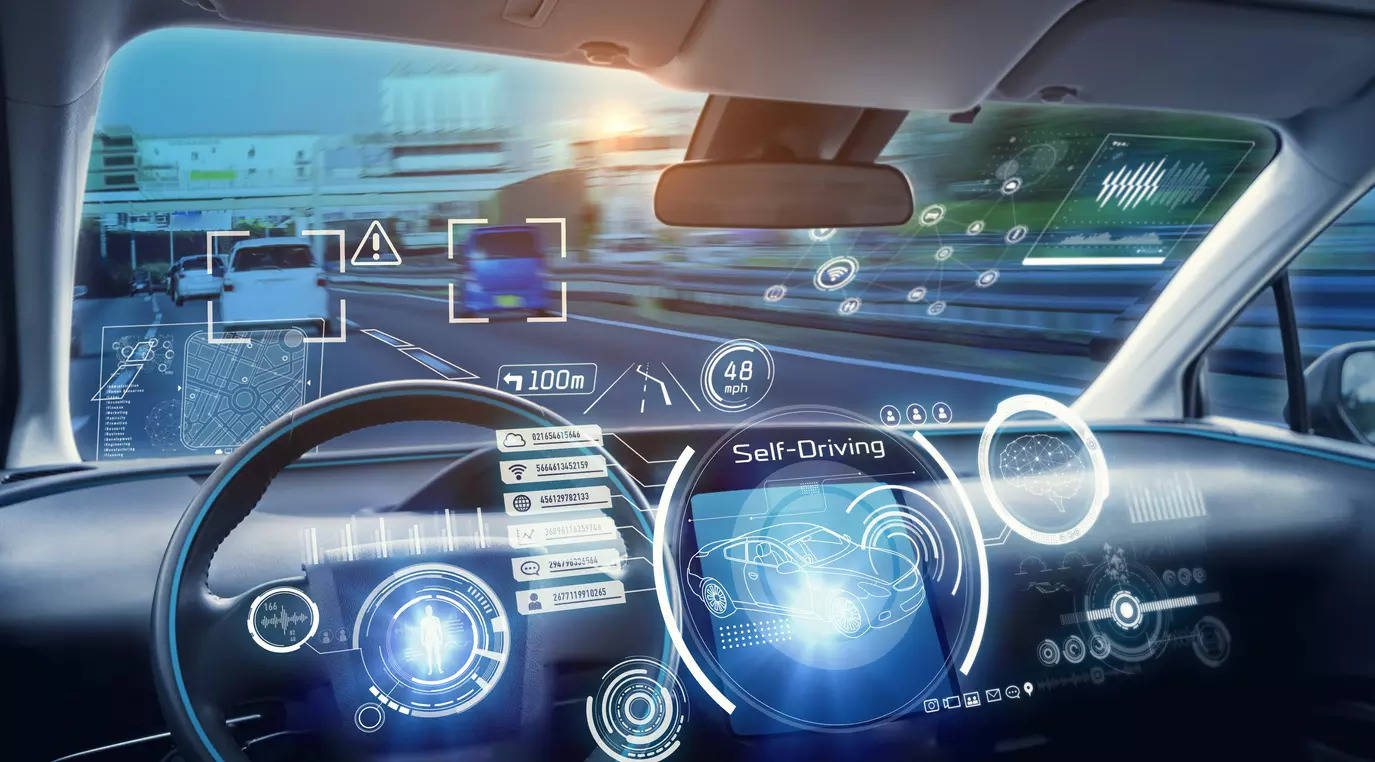
New Delhi: In recent times, the Indian automotive business has witnessed vital developments in driving applied sciences. With the rise of synthetic intelligence (AI) and machine studying (ML), vehicles have gotten smarter and extra able to performing advanced duties with out human intervention.
Some of the notable developments is the proliferation of autonomous driving applied sciences, the place vehicles are geared up with sensors, cameras, and superior applied sciences like ADAS to understand their environment and make clever selections. Moreover, developments in connectivity have remodeled vehicles into cell hubs, enabling seamless integration with smartphones, navigation programs, and different sensible units.
In accordance with a report by Allied Market Analysis, the worldwide autonomous car market was valued at USD 76.13 billion in 2020 and is projected to achieve USD 2,161 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 40.1% from 2021 to 2030, creating a worldwide transformation in transportation. Whereas these figures spotlight the immense potential and market demand for autonomous driving applied sciences, we nonetheless have an extended approach to go earlier than we obtain full autonomy in automobiles.
Let’s dive deep into the present stage of vehicles in India and the way we are able to up our sport to maintain up with world gamers:
Autonomy stage in India vs. different nations
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has categorised autonomous driving into six ranges, starting from Stage 0 to five. The SAE classification gives a transparent framework for understanding the completely different ranges of automation in vehicles. Stage 0 represents automobiles with no autonomous options, whereas Stage 1 contains primary driver help programs akin to adaptive cruise management. Stage 2 introduces partial automation, enabling the automobile to manage steering and acceleration concurrently underneath sure circumstances, with the driving force accountable for monitoring. Stage 3 represents conditional automation, the place the car can handle most facets of driving however might require human intervention in particular conditions. Ranges 4 and 5 contain excessive automation and full automation, respectively, the place the car can deal with all driving duties with none human enter.As of now, India predominantly operates at Stage 1 and Stage 2 automation. Many automobiles within the Indian market supply options like adaptive cruise management, lane-keeping help, and automatic emergency braking. Nevertheless, these programs require fixed driver consideration and intervention, limiting the autonomy of the car.
When in comparison with nations like the US, Germany, and Japan, India remains to be lagging by way of autonomous driving capabilities. These nations have made vital progress in creating and deploying Stage 3 and better automation applied sciences. For example, firms like Tesla, BMW, and Toyota have launched semi-autonomous options that enable their automobiles to carry out advanced maneuvers with out steady driver intervention.
Shifting from Stage 2 to three
To maneuver from Stage 2 to Stage 3 vehicles, India must embrace superior applied sciences akin to sensor fusion, AI, ML, and improved connectivity. Sensor fusion combines knowledge from numerous sensors like Radar and LiDAR to create a complete view of the car’s environment. AI and ML algorithms can analyze this knowledge and make real-time selections, enhancing the car’s means to navigate advanced environments. Moreover, improved connectivity by V2X (vehicle-to-everything) communication can allow vehicles to change info with different automobiles, infrastructure, and pedestrians, enhancing security and effectivity.
Position of semiconductors
Semiconductors play an important function in enabling superior automotive applied sciences. They energy the digital programs that management autonomous options, course of knowledge from sensors, and execute AI algorithms. At the moment, stage 2 automobiles possess superior driver help programs (ADAS) that require semiconductors for capabilities like adaptive cruise management and lane-keeping help.
Nevertheless, the transfer to stage 3 autonomy, the place the car can deal with most driving duties independently, calls for much more superior semiconductors for real-time decision-making, sensor fusion, and complicated algorithms. These semiconductors allow the mixing of lidar, radar, and digicam programs, permitting automobiles to understand their environment precisely and make knowledgeable selections. As India strives to undertake increased ranges of autonomous know-how, the event and adoption of specialised automotive-grade semiconductors will probably be important to make sure reliability, effectivity, and security in autonomous automobiles.
Challenges
A number of challenges must be addressed for a profitable transition. Firstly, infrastructure improvement is essential, together with the set up of strong communication networks and sensible site visitors administration programs. Secondly, high-speed networking and wi-fi connectivity, akin to 5G networks and Wi-Fi 6, play an important function in autonomous automobiles’ functioning. Multi-Gigabit Ethernet with time-sensitive networking (TSN) ensures high quality of service (QoS) and permits seamless knowledge sharing throughout the car are some facets of know-how which can be nonetheless not widespread in India.
Moreover, guaranteeing knowledge privateness and cybersecurity will probably be essential, as autonomous automobiles depend on intensive knowledge sharing. Furthermore, public acceptance and belief in autonomous automobiles have to be fostered by consciousness campaigns and stringent security laws.
The best way ahead
The Indian authorities has acknowledged the potential of autonomous driving and has taken a number of initiatives to advertise its improvement. The Nationwide Electrical Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) and Nationwide Automotive Coverage, which goals to create a positive setting for automotive analysis, improvement, and manufacturing are a few of the few initiatives to speed up the transformation. The federal government ought to proceed to offer supportive insurance policies and incentives for analysis and improvement in autonomous driving applied sciences. Collaborations between academia, business, and analysis establishments will probably be important to foster innovation and information change.
In conclusion, whereas India is at present working at Stage 2 automation, the transition to Stage 3 and past requires vital technological developments. Moreover, with the suitable authorities insurance policies, business collaborations, and public assist, India can efficiently transfer in the direction of increased ranges of autonomy within the automotive sector, remodeling the best way we journey and enhancing security and effectivity on the roads.
(Disclaimer: Hitesh Garg is the Vice President and the India Managing Director of NXP Semiconductors. Views are private.)