New Delhi: Together with the electrification megatrend, R&D efforts to develop extra environment friendly and reasonably priced options are additionally on the rise. The scientists from the Centre for Automotive Power Supplies on the Worldwide Superior Analysis Centre for Powder Metallurgy & New Supplies (ARCI), an autonomous Analysis and Improvement Centre of the Division of Science and Expertise (DST), Authorities of India, have fabricated improved low-cost heavy uncommon earth-free excessive Neodymium Iron Boron (Nd-Fe-B) magnets, that are in excessive demand for electrical automobiles (EV) and might make them extra reasonably priced.
ARCI is establishing a pilot plant to fabricate close to net-shaped Nd-Fe-B magnets by means of a serious challenge funded by the Science and Engineering Analysis Board (SERB) in keeping with the Authorities of India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat mission. The above technique might be explored for the magnets manufactured within the pilot plant.
The brand new technique may be used for industrial manufacturing of Nd-Fe-B magnets in India, lowering imports that meet the key necessities of the automotive sector.
EVs now use BLDC motors
Greater than 90% of EVs use brushless DC (BLDC) motors made up of uncommon earth Neodymium Iron Boron (Nd-Fe-B) magnets. Since its discovery by the Japanese scientist and entrepreneur Masato Sagawa in 1984, the Nd-Fe-B magnet has been one of the sought-after everlasting magnetic supplies for a lot of functions attributable to its distinctive mixture of magnetic properties.
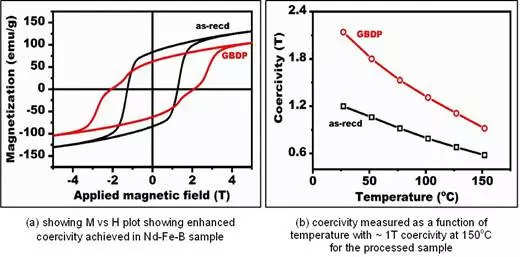
Nd-Fe-B magnets utilized in EVs function at excessive temperatures of 150 – 200oC and have to exhibit excessive resistance to demagnetization, a functionality that pure Nd-Fe-B magnets should not have. Therefore Dysprosium (Dy) metallic is added as an alloy to enhance the resistance to demagnetization. World over, researchers are attempting to boost coercivity (resistance to demagnetisation) of Nd-Fe-B magnets with out the addition of expensive Dy. A technique adopted by the analysis neighborhood to boost coercivity is to counterpoint the area between the grains of the Nd-Fe-B magnet with “non-magnetic” parts by means of appropriate warmth remedies (grain boundary diffusion).
The ARCI scientists have enhanced the coercivity of Niobium (Nb)-containing Nd-Fe-B melt-spun ribbon by grain boundary diffusion course of (GBDP) utilizing a low melting level alloy of Nd70Cu30 which acts because the supply for the “non-magnetic” component. They’ve reported restricted grain progress throughout grain boundary diffusion as a result of precipitation of Nb, which facilitates the enrichment of copper (Cu) on the grain boundaries aiding the elevated resistance to demagnetization of Nd-Fe-B powders.
The coercivity worth of 1 T at 150oC essential for automotive functions achieved on this analysis printed in Supplies Analysis Letter might be a helpful technique to develop magnets with out Dy for EV functions.
Additionally Learn: