Welcome to half three of our deep dive sequence into the Perodua Ativa (often known as the D55L), the place the main focus this time is on the transmission that might be utilized by the compact B-segment SUV.
Based mostly on all the knowledge we’ve thus far, it’s identified that the Ativa may have fairly a bit in frequent with the Daihatsu Rocky and Toyota Raize. This consists of the usage of the 1KR-VET 1.0 litre turbocharged three-cylinder petrol engine and the Daihatsu New World Structure (DNGA), the previous of which is paired with a D-CVT.
We’ve already talked concerning the 1KR-VET and DNGA in components one and two, so if you wish to know extra about both of them, simply click on on the hyperlinks above. On this submit, we’re discussing the Ativa’s D-CVT, which isn’t solely the primary for a Perodua mannequin, however is completely different from a traditional CVT. What does the “D” stand for? How does it function? Learn on to seek out out.
D-CVT – Twin mode CVT, world’s first split-gear system
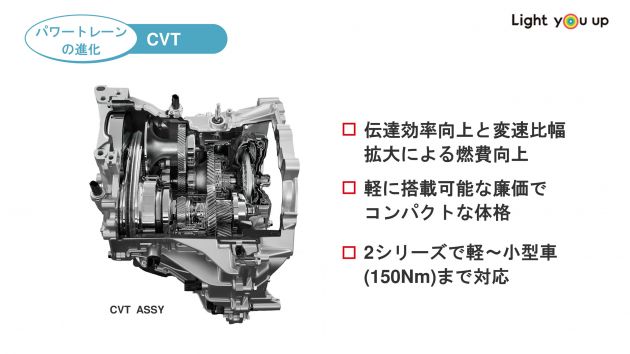
Daihatsu’s full advertising time period for its D-CVT is Twin mode CVT, and the transmission first made its debut alongside the DNGA platform with the fourth-generation Tanto kei MPV again in July 2019. On the time, the corporate claimed the D-CVT was the world’s first split-gear CVT system that mixes belt drive with a gear drive, leading to improved gas effectivity, acceleration really feel and tranquility.
The Raize, which shares the identical transmission, was publicised because the the very first Toyota mannequin to make use of D-CVT expertise in 2019.
Why a CVT is good for small vehicles
Earlier than entering into what Daihatsu is on about, let’s begin with the basics. In a typical CVT, there may be an enter pulley that’s related to the engine crankshaft via a torque converter (or clutch pack) and an output pulley that sends energy to the wheels. A belt (or chain) connects the 2 pulleys, which may alter their diameters to offer an infinite variety of gear ratios.
With none gears, the stepless transmission permits for smoother acceleration and effectivity, whereas being smaller in dimension in comparison with transmissions that do have gears. This can be a good set of traits for Daihatsu, because it permits for higher packaging in its kei and compact vehicles.
However there are downsides to a standard CVT
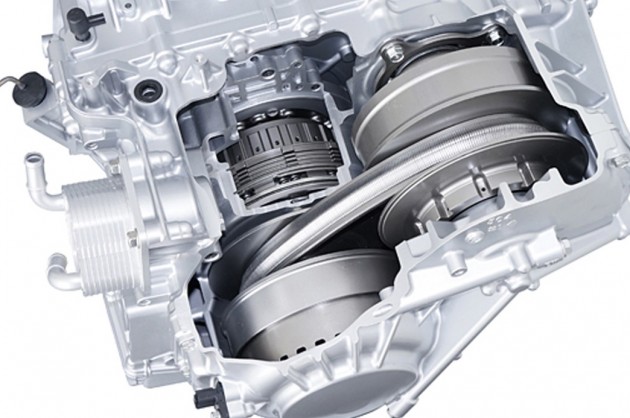

Nonetheless, there are some downsides, as CVTs usually expertise power losses as a result of friction (of the belt or chain) as in comparison with geared transmission. That’s not all, as CVTs deliver with them a standard whining sound as a result of all that belt-on-pulley motion, which is extra profound when it has to take care of heavy masses like throughout arduous acceleration or excessive speeds.
Moreover, a CVT will all the time need to maintain the engine working inside its peak output rpm by various its gear ratio accordingly, which is why the engine sounds “tortured” because the automobile will get up to the mark, even when it isn’t – that’s simply the way in which it really works.
At greater speeds like whereas freeway cruising, the CVT is at its highest doable ratio, which could nonetheless outcome within the engine being at a excessive rev level that isn’t good for gas financial system. One technique to develop the gear ratio vary of a CVT is by rising the scale of the pulleys, though that is counterintuitive if the unit needs to be small.
D-CVT shifts from belt to gears on greater load
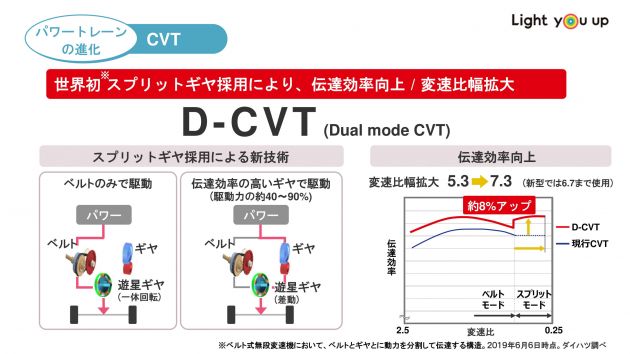
In contrast to standard CVTs, Daihatsu’s D-CVT doesn’t simply depend on belt drive, however introduces cut up gears into the combination. As you’ll be able to see from the cutaway of the D-CVT, there are further gears and a planetary gear set fitted to the enter and output shafts of the pulleys, with a clutch pack to interact or disengage the latter.
In regular operation, whenever you’re pulling off from a cease and travelling as much as low to medium speeds, the D-CVT capabilities like every other CVT, with the belt drive doing the entire work to get energy from the engine to the wheels.
Nonetheless, whenever you stand up to greater speeds (Daihatsu says between 40-90% driving drive in its presentation), the D-CVT shifts into its cut up mode, participating the gear drive that gives a extra environment friendly (much less power loss) technique of energy transmission, whereas the rotation to the belt drive is decreased considerably.
You’ll be able to see this transition between regular and cut up mode in a video by Japan’s Internet Cartop above. At low to medium speeds, the belt drive is totally engaged, however at greater speeds, the D-CVT’s clutch pack brings the gear drive into operation, relieving the belt drive.
Not Toyota’s Direct Shift-CVT, however a completely completely different Twin mode CVT
Whereas each the D-CVT and Direct Shift-CVT have further gears in them, Toyota’s strategy is completely completely different because it provides on a launch gear that acts like a primary gear in a traditional transmission. The launch gear is used when setting off from a cease, earlier than the transmission switches to belt drive like a CVT as a substitute. This was designed to supply a extra direct drive connection at low speeds.
In a manner, the D-CVT is sort of a “flipped” model of the Direct Shift-CVT, as gear drive is used at greater speeds relatively than for setting off. So, why not simply adapt Toyota’s expertise then? Effectively, including a gear selector to interact the launch gear will increase the complexity of the transmission, which could possibly be pricey and wouldn’t be appropriate for funds autos.
Higher transmission effectivity, decrease rpm, gear ratio vary equal to an eight-speed automated
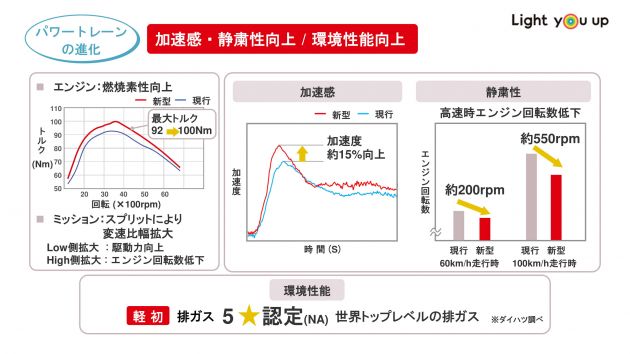
It’s all details and figures at this level, as Daihatsu says the cut up gears enable the gear ratio vary of the D-CVT to be prolonged on each high and low sides from 5.3 to 7.3. On the low facet, it has the next variety of brief ratios to deal with acceleration, whereas on the opposite finish, excessive ratios enable it to be higher fitted to high-speed cruising.
The corporate notes {that a} standard CVT’s gear ratio vary is usually equal to that of a standard six-speed automated, however the D-CVT in cut up mode is nearer to an eight-speed unit as a substitute. That is achieved purely due to the cut up gears, as there’s no have to make pulleys bigger for a wider gear vary ratio.

In comparison with an everyday CVT, the D-CVT in cut up mode experiences much less power losses because the friction that comes with the belt drive in play is eliminated. This leads to improved transmission effectivity by 12% at 60 km/h and by 19% at 100 km/h.
The engine velocity can also be diminished by at these speeds by 200 rpm and 550 rpm respectively, so that you hear much less of the engine at work and profit from higher gas consumption too. Daihatsu additionally claims that drivers may have 15% higher acceleration really feel, which ought to cut back the “sluggishness” that folks really feel when utilizing regular CVTs.
Extremely compact, smallest on the earth, however with max torque restrict of 150 Nm
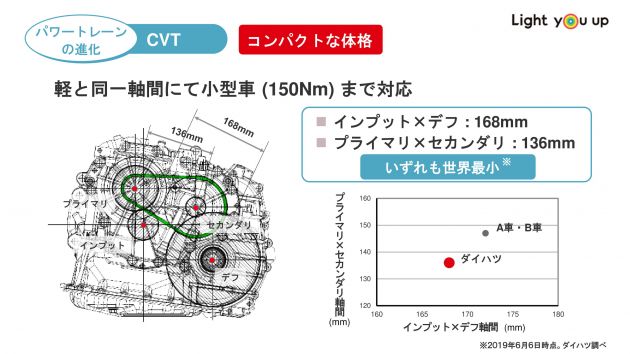
For extra figures, the corporate says that the gap between the centre of the enter and output pulleys within the transmission is simply 136 mm, whereas the gap between the centre of the transmission’s enter and output factors is simply 168 mm, each claimed to be the smallest on the earth.
Limitations? Like different CVTs and regular transmissions, the D-CVT is can solely deal with a specific amount of torque, which is as much as 150 Nm. Daihatsu says its transmission is optimised for use in all fashions from mini (kei vehicles) to autos with engine capacities of as much as 1.5 litres.
Since kei vehicles are restricted to 660 cc by regulation, with a max output of 64 PS (63 hp), the D-CVT is greater than as much as the duty. As for the 1KR-VET within the Ativa, it makes 98 PS (97 hp) and 140 Nm, which is properly inside bounds of the D-CVT, so the pairing is properly throughout the limits.
So, the impact on driving expertise?
To summarise, the D-CVT ought to provide clean acceleration as much as medium speeds, however with higher gas consumption and a quieter drive at excessive speeds. It’s extra compact, has a wider vary of ratios and permits for decrease rpms at cruising speeds, with diminished belt friction/slip losses. Perodua claims a class-leading gas consumption determine of 18.9 km per litre.
Nonetheless, as you will notice within the video above, it nonetheless behaves like a standard CVT on full throttle conditions, the place it holds on to a really excessive rev (between 5,500 to six,000 rpm) below arduous acceleration. It doesn’t simulate any gear modifications like sure newer CVTs from Toyota and Nissan. Now that is one thing customers must get used to, particularly in the event that they’re coming from a standard torque converter automated like Perodua’s personal 4AT.
Curiously, the Rocky and Raize have a Energy button on the steering wheel, which remaps the engine and gearbox for faster throttle response. It’s unclear, nonetheless, if the Perodua model will include the identical operate.
CVT is the way in which ahead for Perodua

With all this info, it’s clear that D-CVT is the way in which ahead for Daihatsu and Perodua. It’s a model new transmission expertise designed alongside the DNGA platform, and will probably be utilized in most, if not all new product launches any longer. So, prefer it or not, D-CVT is right here to remain.
Whereas it’s unlikely that the present Perodua fashions will shift from 4AT to D-CVT anytime quickly, the following generations fashions will very doubtless function the brand new transmission, beginning with the rumoured DNGA-based new D27A Alza.
So, armed with this data, what do you consider the Perodua Ativa’s D-CVT?
GALLERY: Daihatsu Rocky in Japan
GALLERY: Toyota Raize in Japan









