Recognized for its excessive power density and lengthy cycle life, lithium-ion has emerged as the popular selection of battery expertise. Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are additionally distinguished by their adaptability and scalability, rendering itself to be an excellent candidate for functions in electrical automobiles (EV) and utility-scale power storage. The convergence of the technical advantages coupled with swift growth of world manufacturing capacities for LIBs has resulted in a considerable discount in manufacturing prices.India is actively selling battery manufacturing and provide chain growth, however its entry to battery essential minerals, particularly lithium, important for cathode and electrolyte, stays severely restricted. To beat this, the Indian authorities has initiated efforts to safe essential mineral provides by way of partnerships such because the Mineral Safety Partnership (MSP) and SPVs like KABIL.
Nonetheless, provide vulnerabilities stay. China is the dominant participant throughout the worth chain together with provide of minerals resembling lithium and graphite. In 2023, China restricted graphite exports, disrupting provide chains for international locations just like the US and South Korea. Though India is scaling up its graphite and anode capability, lithium provide stays closely uncovered to geopolitical dangers due to heavy backward integration of 5 to seven high Chinese language lithium processing corporations into mining in Australia and Chile. As well as, China is planning to limit export of superior applied sciences, significantly these associated to lithium refining and cathode preparation.
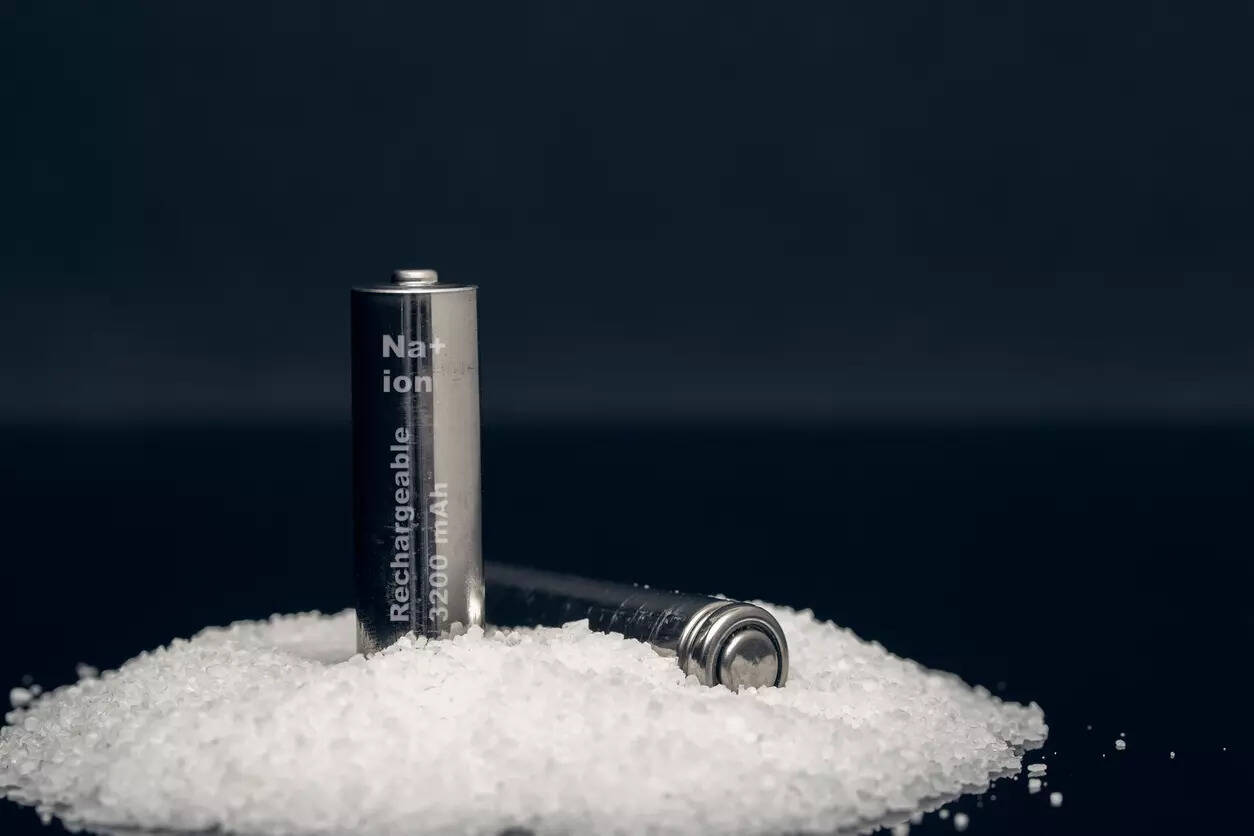
Given the restrictions and challenges surrounding essential minerals and battery expertise, Indian stakeholders, together with the federal government and trade, must realign their methods to safe a resilient place within the international battery provide chain. On this context, sodium-ion batteries (SIBs), although nonetheless within the growth stage, current a promising different among the many accessible battery chemistries.
Comparability: LIBs and SIBs
- Cathode Energetic Materials (CAM): SIBs usually make the most of cathode supplies designed to accommodate the bigger sodium-ions, resembling Layered Oxides, Polyanionic compounds, or Prussian Blue analogues. LIBs usually use lithium iron phosphate (LFP) or different lithium containing compounds.
- Anode Energetic Materials (AAM): Whereas graphite is the widespread anode materials for LIBs, it’s not as efficient for SIBs as a result of sodium ions don’t intercalate as readily into graphite. Different supplies for SIBs, embody arduous carbon and mushy carbon.
- Electrolyte salts: The electrolyte in SIBs accommodates sodium salts, resembling sodium hexafluorophosphate (NaPF6), whereas LIBs use lithium salts like lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6). The solvents and components may differ to optimize efficiency.
- Different cell elements resembling separators, aluminium foil, and casings are basically widespread throughout LIBs and SIBs.
Techno-commercial suitability of SIBs
The largest benefit of SIBs lies within the abundance of sodium, one in every of Earth’s most plentiful components. Whereas LIBs are at the moment cheaper, SIBs when produced at scale can doubtlessly be ~20per cent to 30per cent extra economical.Though SIBs have a decrease power density, they provide superior security and temperature tolerance, making them match for Battery Power Storage Methods (BESS). Prioritising early adoption of SIBs in BESS can drive down prices, paving the way in which for his or her eventual growth into mobility functions.
India’s superior chemical trade is well-positioned to provide important SIB elements, strengthening the home provide chain. SIBs are additionally appropriate with current LIB infrastructure (cell manufacturing), enabling a clean transition with minimal funding.
Nonetheless, to grasp the potential of SIBs, India wants a strategic and multi-faceted method. Key stakeholders ought to take decisive steps to advance each the technological maturity and commercialisation of SIBs.
Expertise maturity: The federal government can prioritize larger funding for educational and industrial analysis targeted on enhancing power density, cycle life, and materials traits. Along with current pilot infrastructure, constructing accessible pilot strains might help bridge the hole between laboratory analysis and full-scale manufacturing. Cultivating partnership between pilot strains and established organizations, resembling Automotive Analysis Affiliation of India (ARAI) and third-party amenities, can additional expediate prototype testing and validation of SIB expertise.
Creating incubators and innovation hubs can catalyse technological breakthroughs and supply assets, mentorship, and assist for startups and researchers within the battery area. As well as, leveraging IP rights to create strategic partnerships and licensing agreements can additional encourage a steady cycle of innovation and investments in SIB.
Commercialisation roadmap: The federal government can prioritize the allocation of the remaining 10 GWh beneath the ACC PLI scheme to gamers choosing different chemistries like SIBs to expediate commercialisation. The rollout of incentives resembling tax breaks for uncooked supplies, streamlined approvals to determine manufacturing amenities, and assist for OEMs to conduct PoC tasks will be essential in bridging between R&D and business deployment.
The trade can even leverage worldwide partnerships with international battery gamers primarily based in Japan or Korea. Having access to superior applied sciences and making a collaborative effort among the many Indian chemical trade, Tier-1 producers, and educational establishments will assist forge a strong provide chain for SIBs.
Moreover, constructing focused coaching modules on cell expertise, the utilization of kit when scaling a gigafactory, and high quality management shall be key to cultivating a specialised proficient workforce in battery expertise inside India.
Adopting a twin technique
Nearly all of SIB gamers are at a Expertise Readiness Degree (TRL) of 5 to six, which is way from the business deployment ranges of 8 to 9. Within the interim, it’s prudent for India to actively take part within the power transition by utilising LIBs whereas concurrently getting ready to embrace a forward-thinking technique by way of the combination of SIBs. This dual-track method will allow India not solely to take part within the international power transition however to guide it, particularly as SIBs attain business maturity and provide a viable different to the present LIB paradigm.